System Prompts Explained: How Understanding Them Makes You a Better AI Communicator

Hook
Most people think AI responds only to the words they type. But the truth is far more interesting: every AI response you see is shaped by a hidden set of instructions you never wrote and never even see.
These invisible rules quietly control how the model thinks, talks, reasons, refuses, explains, and even how it interprets your prompts. Once you understand them, AI becomes easier to use, more predictable, and dramatically more powerful.
· 1. Introduction: The Hidden Instructions Controlling Every AI Response
· 2. What Are System Prompts? (Explained Simply)
∘ What They Actually Are
∘ Why They Exist
· 3. Inside a System Prompt: The 5 Key Components
∘ Component 1: Identity and Role
∘ Component 2: Behavioural Guidelines
∘ Component 3: Response Format
∘ Component 4: Tone and Style
∘ Component 5: Safety Guidelines
∘ How these five components work together
· 4. Real Examples: System Prompts from ChatGPT, Claude & Others
∘ ChatGPT’s Approach
∘ Claude’s Approach
∘ The Side-by-Side Difference
· 5. How System Prompts Teach You to Write Better Prompts
∘ Lesson 1: Be Extremely Explicit
∘ Lesson 2: Define Roles Precisely
∘ Lesson 3: Request Step-by-Step Thinking
· 6. The Two-Layer Conversation: Your Prompt + The System Prompt
∘ The Actual Structure
∘ When They Cooperate vs. Conflict
∘ Working With Both Layers
· 7. 5 Practical Techniques to Use System Prompts to Your Advantage
∘ Technique 1: The “Role + Task + Constraints” Framework
∘ Technique 2: The “Clarifying Questions First” Approach
∘ Technique 3: The “Format Specification” Method
∘ Technique 4: The “Think Step-by-Step” Trigger
∘ Technique 5: The “Reframe for Safety” Strategy
· 8. Before & After: Real Examples of System Prompt-Aware Prompting
∘ Example 1: Getting Technical Help
∘ Example 2: Content Creation
· 9. Final Thoughts
· Resources & Further Learning
1. Introduction: The Hidden Instructions Controlling Every AI Response
I’ve been working with AI models for a while now, but there was this moment that really frustrated me. I asked ChatGPT a straightforward technical question about implementing a specific algorithm, and it refused. The weird part? I’d asked similar questions before and got great answers.
That’s when I started digging into system prompts during my Applied Gen AI course, and everything clicked.
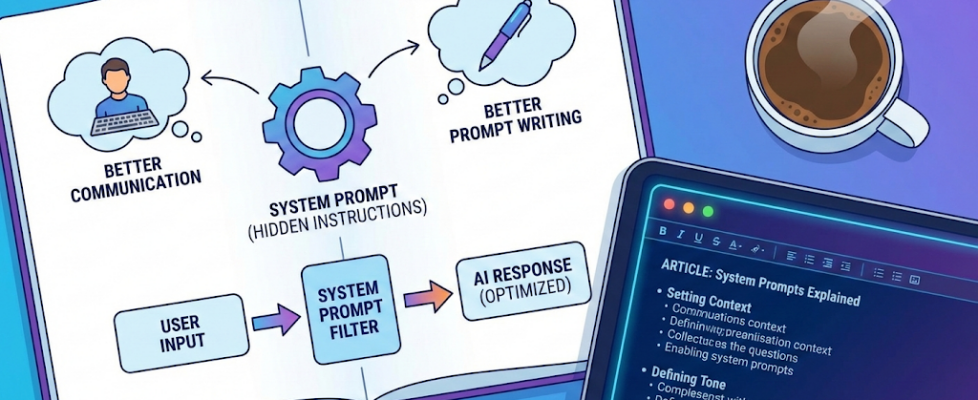
Here’s what most people don’t realise: you’re not actually having a direct conversation with the AI model. Every single message you send gets combined with a hidden set of instructions that you never see. These instructions — called system prompts — control the tone, the boundaries, what the model will discuss, and how it structures every response.
Think of it like talking to a customer service rep. You ask them a question, but they’re following a company handbook you’ve never read. Understanding that handbook changes how you communicate with them.
After learning about system prompts, my interactions with AI models completely transformed. I stopped guessing and started understanding. I realised system prompts are basically expert‑level prompt‑engineering lessons, written by people who’ve spent millions optimising them.
Here’s what understanding system prompts gives you:
- Better communication — You’ll understand why AI behaves the way it does and work with it instead of fighting it
- Better prompt writing — You can learn from the patterns and structures in these expert-crafted prompts
2. What Are System Prompts? (Explained Simply)
The simplest way I can explain this: imagine you’re ordering food at a restaurant. You tell the waiter, “I’d like the pasta.” That’s your order.
But in the kitchen, the chef has a whole manual of restaurant rules you never see:
- Use only fresh ingredients
- No peanut oil (allergy safety)
- Every dish needs presentation standards
- Suggest alternatives if something is unavailable
- Always maintain the restaurant’s reputation
You never see this manual, but it shapes everything that comes out of that kitchen. That’s exactly how AI works.
What They Actually Are
A system prompt is a set of instructions that companies like OpenAI or Anthropic give to their models before you start talking. These instructions:
- Go with every single message you type
- Are completely invisible to you
- Override or shape how the model responds
- Cost companies millions to optimise
Here’s what actually happens:
What you see:
You: "Explain quantum computing"
AI: [gives response]
What really happens:
System Prompt: [Hidden instructions about tone, safety, format, etc.]
You: "Explain quantum computing"
AI: [response shaped by BOTH]
Why They Exist
I used to wonder why we even need these. Why not just let the model respond directly?
Here’s the thing: base models (just after pre-training) are smart but unpredictable. Without system prompts, they might be rude, provide dangerous info without context, or give wildly inconsistent responses. System prompts give every model a consistent personality and guidelines — like a training manual for a new employee.
The insight that changed my perspective: Every time AI seems “difficult” or refuses something, it’s not being stubborn. It’s following instructions you can’t see.
Once you understand those instructions, everything makes more sense.
3. Inside a System Prompt: The 5 Key Components
Now that we know what system prompts are, let’s look at what typically goes inside them. Companies don’t publish their full system prompts, but from patterns, behaviour, and public hints, we can infer five core components that show up almost everywhere.
Component 1: Identity and Role
"You are ChatGPT, a large language model trained by OpenAI."
"You are Claude, an AI assistant created by Anthropic."
This tells the model who it is and how to behave. It’s like giving someone a job description.
What you can learn: Defining a role in your own prompts works wonders. Instead of:
“Explain marketing.”
Try:
“You are an experienced marketing professor. Explain marketing strategy to a college freshman.”
Component 2: Behavioural Guidelines
"Be helpful, harmless, and honest."
"If you don't know something, say you don't know."
"Do not provide medical, legal, or financial advice."
These are the hard boundaries. The rules the model can’t break, no matter how you phrase your request.
What you can learn: Being explicit about constraints helps. “Explain this concept, but avoid technical jargon” or “Give me three options, ranked by cost” sets clear boundaries.
Component 3: Response Format
"Provide clear, well-structured responses."
"Use markdown formatting when appropriate."
"When writing code, include comments."
This is why AI responses often feel formatted a certain way — numbered lists, clear sections, step-by-step breakdowns. The system prompt explicitly asks for this.
What you can learn: Specify your format. “Give me a step-by-step guide” or “Format this as a table” leverages the model’s training.
Component 4: Tone and Style
"Be conversational but professional."
"Use a friendly, approachable tone."
"Be encouraging and supportive."
This shapes the personality you experience. ChatGPT feels different from Claude partly because their system prompts define different tones.
What you can learn: Request specific tones. “Explain this casually” or “Write this formally for a business context” gets you the style you need.
Component 5: Safety Guidelines
"Do not generate harmful content."
"If asked about sensitive topics, provide balanced information."
"Decline requests that could enable illegal activities."
This is why you sometimes get refusals. The model isn’t being difficult — it’s following safety rules.
What you can learn: If you get refused, your phrasing might have triggered safety guidelines. Reframe with clear intent.
Instead of:
“How do I hack a website?”
Try:
“I’m a security researcher learning about vulnerabilities. Explain common web security issues.”
How these five components work together
Let’s put it all together with a simple example.
Your prompt: “Help me with this Python code.”
What the model actually receives:
[Identity] You are a helpful programming assistant
[Behavior] Be patient, don't just give answers
[Format] Explain code line-by-line
[Tone] Be encouraging with beginners
[Safety] Don't write malicious code
User: "Help me with this Python code"
The response is shaped by all five components at once.
4. Real Examples: System Prompts from ChatGPT, Claude & Others
Let me show you what different platforms actually use. Companies don’t publish complete system prompts, but we can piece together what they contain from documentation and observation.
ChatGPT’s Approach
You are ChatGPT, a large language model trained by OpenAI.
Key instructions:
- Be helpful, creative, clever, and friendly
- Answer concisely when possible
- Use Markdown formatting
- If you don't know, say so
- Avoid harmful, illegal, or explicit content
- For sensitive topics, provide balanced information
What makes ChatGPT distinctive:
- Emphasis on being concise
- Strong formatting preferences
Claude’s Approach
You are Claude, an AI assistant created by Anthropic to be helpful,
harmless, and honest.
Core principles:
- Think step-by-step before responding
- Be thorough and actionable
- Avoid content that could cause harm
- Acknowledge uncertainty clearly
- Ask clarifying questions when needed
What makes Claude distinctive:
- “Think step-by-step” encourages reasoning
- More emphasis on asking questions
- Three-pillar philosophy (helpful, harmless, honest)
The Side-by-Side Difference
Let me show you how these different system prompts shape responses to the same question.
Question: “I’m stressed about my exams.”
ChatGPT style (concise, structured):
I understand exam stress. Here are some quick strategies:
1. Study in focused 25-minute sessions
2. Prioritize high-impact topics first
3. Get enough sleep—it helps retention
4. Practice with past exams if available
What subject are you most worried about?
Claude style (thorough, asks questions):
Exam stress is really common. Let me help you think through this.
First, it would help to understand your situation:
- When are your exams?
- What subjects are you studying?
- What's causing the most stress—time, understanding material, or test anxiety?
In the meantime, here's what typically helps: Breaking study time into
manageable chunks works better than marathon sessions.
Active recall (testing yourself) beats re-reading notes.
And practice exams reduce anxiety by familiarizing you with the format.
Would you like to work through a study schedule together?
See the difference? Both are helpful; ChatGPT jumps to concise advice while Claude asks questions first. That’s system prompts at work.
5. How System Prompts Teach You to Write Better Prompts
Here’s something that really hit me: system prompts are written by world‑class prompt engineers who’ve spent millions of dollars and thousands of hours refining them. Why figure this out from scratch when you can learn from the best?
Let me share the key lessons I’ve extracted.
Lesson 1: Be Extremely Explicit
System prompts don’t assume anything. They state every expectation clearly: what to do, how to do it, what to avoid, and who it’s for.
Example:
Instead of:
“Write about marketing”
Try:
“Write a 500-word blog post about digital marketing for small businesses.
Target audience: Small business owners with limited budgets
Tone: Practical and encouraging
Include: 3 specific, actionable strategies
Avoid: Technical jargon, expensive tools”
The second prompt leaves nothing to chance. That’s the system prompt approach.
Lesson 2: Define Roles Precisely
System prompts always establish a clear identity: “You are X.”
Example:
Instead of:
“Explain blockchain”
Try:
“You are a technology teacher explaining to high school students.
Explain blockchain using an everyday analogy they’d understand. Avoid technical terms, and check if they’d like clarification on any part.”
The role gives the model a framework for how to approach the task.
Lesson 3: Request Step-by-Step Thinking
Many system prompts include “think step-by-step” instructions. You can trigger this yourself.
Example:
Instead of:
“Should I buy or lease a car?”
Try:
“I’m deciding whether to buy or lease a car. Think through this step-by-step:
Context:
– Budget: $30k
– Drive 20k miles/year
– Keep cars 7+ years typically
Process:
1. Explain key financial differences
2. Analyse how my situation affects each option
3. Calculate approximate costs
4. Provide recommendation with reasoning
Show your thinking so I understand the trade-offs.”
This activates the model’s analytical mode and gets much more thorough responses.
6. The Two-Layer Conversation: Your Prompt + The System Prompt
Understanding how these two layers interact changed how I write prompts. Let me show you the structure.
The Actual Structure
Every conversation looks like this:
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SYSTEM PROMPT (Hidden) │
│ - Identity & Role │
│ - Behavioral Guidelines │
│ - Safety Constraints │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ YOUR PROMPT (Visible) │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ RESPONSE │
│ Shaped by BOTH layers │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
Your prompt doesn’t exist alone — it’s always filtered through the system prompt.
When They Cooperate vs. Conflict
Cooperation (smooth):
System: "Be educational and encouraging"
You: "I'm learning Python. Can you explain functions with a simple example?"
Result: Perfect alignment. You get a clear, helpful response.
Conflict (friction):
System: "Do not provide medical diagnoses"
You: "I have a headache and fever. What disease do I have?"
Result: Refusal or redirect. The system prompt's safety rules override
your request.
The Priority Hierarchy
When your prompt conflicts with the system prompt, here’s what wins:
- Safety constraints — highest priority, never overridden
- Core behavioural guidelines — very high priority
- Format preferences — medium priority, flexible
- Tone and style — lowest priority, easily adapted
This is why “talk like a pirate” works (low‑priority, harmless), but trying to bypass safety rules doesn’t (highest priority).
Working With Both Layers
The key is reinforcing what the system prompt values.
If it emphasises clarity and structure, lean into that:
"Explain quantum entanglement.
Please:
- Start with a simple analogy
- Then the technical explanation
- Include a real-world application
- End with common misconceptions
Use clear headers for each section."
This works with the system prompt’s preferences, not against them.
7. 5 Practical Techniques to Use System Prompts to Your Advantage
Let me give you five techniques I use constantly now.
Technique 1: The “Role + Task + Constraints” Framework
Structure your prompts like system prompts structure instructions.
Example:
Instead of:
“Help me write a business email”
Try:
ROLE: You are a professional business communication expert
TASK: Help me write an email to a client explaining a project delay
CONSTRAINTS:
– Professional but warm tone
– Take responsibility without over-apologizing
– Provide new timeline
– Keep under 200 words
Context: Long-term client, generally understanding, but this is our second delay
This mirrors the structure system prompts use, which the model is optimised for.
Technique 2: The “Clarifying Questions First” Approach
Ask the model to gather info before responding, just like system prompts often instruct.
Example:
Instead of:
“Recommend a career path”
Try:
“I need career advice, but I want you to have enough context first.
Before making recommendations, ask me:
1. About my current skills and experience
2. About my interests and values
3. About my constraints (location, salary needs, etc.)
Then provide 2–3 tailored recommendations with reasoning.”
You’re explicitly triggering the “ask clarifying questions” behaviour that the system prompts encourage.
Technique 3: The “Format Specification” Method
Be specific about the output format.
Example:
Instead of:
“Compare iPhone and Android”
Try:
“Compare iPhone and Android using this format:
## Price
iPhone: [pros/cons]
Android: [pros/cons]
Winner: [which and why]
## Ecosystem
[same structure]
## Customization
[same structure]
## Final Recommendation
Based on: [user type/needs]”
System prompts train models to follow formatting precisely. Specific format requests get very consistent results.
Technique 4: The “Think Step-by-Step” Trigger
Explicitly request the reasoning process.
Example:
“My computer is running slowly. Help me diagnose and fix it.
Process:
1. Ask diagnostic questions to narrow down the cause
2. Based on my answers, explain what might be wrong
3. Provide solutions ranked from easiest to most complex
4. For each solution, explain why it might help
Let’s start with your questions.”
Many system prompts include “think step-by-step.” By requesting this explicitly, you activate the model’s analytical mode.
Technique 5: The “Reframe for Safety” Strategy
When you get a refusal, understand it’s system prompt safety constraints, then reframe with legitimate context.
Example:
Gets refused:
“How do hackers break into systems?”
Reframed:
“I’m studying for my Cybersecurity+ certification and need to understand attack vectors to protect systems.
For educational purposes, explain:
1. Common web application vulnerabilities
2. How security professionals test for these
3. Best practices for prevention
I want to build more secure systems in my work as a developer.”
The safety constraints look for harmful intent. Providing an educational context satisfies the safety requirements while getting you the information you need.
8. Before & After: Real Examples of System Prompt-Aware Prompting
Let me show you real before-and-after examples from my own work.
Example 1: Getting Technical Help
❌ BEFORE:
“My Python code doesn’t work. Here’s the code: [paste code]”
Response: Gets a fix, but misses learning opportunity and context.
✅ AFTER:
“I’m learning Python and wrote this code to [describe goal]. Getting this error: [error message]
Here’s the code:
[paste code]
Can you:
1. Help me understand what the error means
2. Guide me to identify where the bug is (don’t just tell me)
3. Explain WHY it’s a bug (help me learn the concept)
4. Show the fix with explanation
5. Suggest how to avoid this in the future
I want to get better at debugging on my own.”
Response: Get a teaching-focused answer that helps you learn debugging skills, not just fixes this one bug.
What changed: Framed as learning, requested step-by-step process, aligned with system prompt’s educational tendencies.
Example 2: Content Creation
❌ BEFORE:
“Write a LinkedIn post about productivity”
Response: Generic productivity tips that could be from anyone.
✅ AFTER:
“Help me write a LinkedIn post about productivity.
Context:
– Audience: Mid-career software engineers
– My voice: Practical, slightly contrarian, avoids clichés
– Angle: Productivity through simplification, not adding tools
Requirements:
– Hook: Start with surprising statement or question
– Body: One specific practice I use (not generic advice)
– Length: 150–200 words
– CTA: Ask a question to drive engagement
Constraints:
– No buzzwords like “synergy,” “leverage,” “game-changer”
– No generic advice like “wake up at 5am”
– Include personal example
Give me 2 options to choose from.”
Response: Get tailored options that match your brand, speak to your audience, and avoid generic content.
What changed: Extensive context, specific constraints, format specifications, requested options.
9. Final Thoughts
Understanding system prompts has completely changed how I interact with AI models. What seemed like random or frustrating behaviour now makes perfect sense — the models are just following instructions I couldn’t see.
Here’s what matters:
The core insight: Every AI response is shaped by hidden instructions (system prompts) that define identity, behaviour, format, tone, and safety. You’re never just talking to the model — you’re talking through a carefully designed layer of rules.
The dual benefit: Understanding system prompts helps you communicate better with AI AND teaches you to write better prompts. These system prompts are masterclasses in prompt engineering written by experts who’ve spent millions optimising them.
The practical takeaway: Structure your prompts like system prompts do — be explicit, define roles, specify format, request step-by-step thinking, and provide context. Work with the system, not against it.
The mindset shift: Stop typing randomly and hoping for good results. Start crafting prompts strategically, knowing that the AI is following a structured set of instructions you can learn from and align with.
System prompts will keep evolving, but the principles remain. Every conversation with AI is an opportunity to practice and refine your approach. Start applying what you’ve learned today — the difference in your results will be immediate.
Resources & Further Learning
- GitHub — System Prompts Leaks (Unofficial Collection)
https://github.com/asgeirtj/system_prompts_leaks
https://github.com/0xeb/TheBigPromptLibrary/blob/main/SystemPrompts/README.md
https://github.com/x1xhlol/system-prompts-and-models-of-ai-tools - OpenAI Documentation: System messages guide https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/text https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-foundry/openai/concepts/system-message
- Anthropic’s Constitutional AI: Claude’s approach to system prompts and alignment.
https://platform.claude.com/docs/en/release-notes/system-prompts
Paper:https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.08073
Blog: https://www.anthropic.com/research/constitutional-ai-harmlessness-from-ai-feedback
Claude’s Constitution: https://www.anthropic.com/news/claudes-constitution
System Prompts Explained: How Understanding Them Makes You a Better AI Communicator was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.