Setting Up TensorFlow with GPU (CUDA): A Step-by-Step Installation Guide
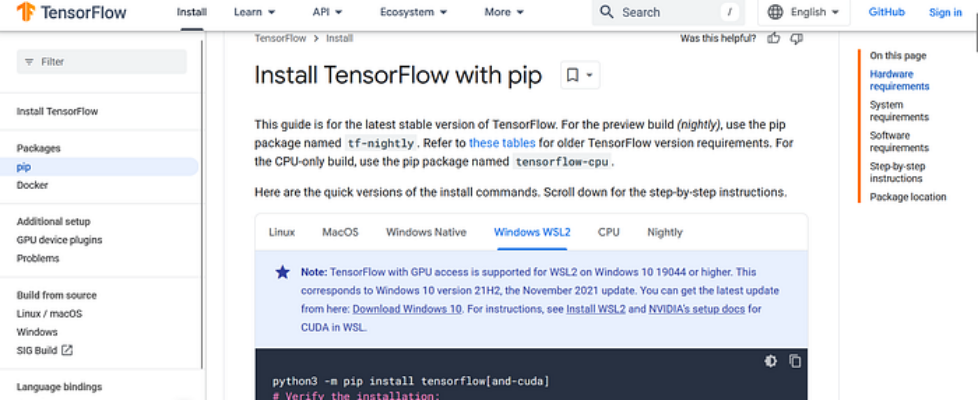
Author(s): Muaaz Originally published on Towards AI. If you are writing Deep Learning code on a machine with a GPU, TensorFlow will default to running on the CPU. This happens because TensorFlow does not automatically select the best hardware. To use the GPU, you must specify it manually. To run TensorFlow code on a GPU, you don’t need any extra setup beyond installing the GPU-enabled version of TensorFlow. However, if you are using Windows, you must install Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) because, starting from TensorFlow 2.10, the GPU version is no longer supported natively on Windows. To install WSL, open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following command: wsl –install After installing WSL, open it from the search bar. The interface should look like this: After opening WSL, run the following commands: The following command checks whether GPU drivers are installed on your system: nvidia-smi Download and install Miniconda using the following command, as we need to create a virtual environment: wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh -O miniconda.sh Run the following installer script: bash miniconda.sh Activate Conda using the following command: source ~/.bashrc Create a Conda environment using the following command: conda create – name tf-gpu python=3.9 -y Activate the TensorFlow GPU environment using the following command: conda activate tf-gpu Install TensorFlow GPU using the following command: pip install tensorflow[and-cuda] Before moving further, I want to mention that to interact with the GPU, we need to install CUDA, which is a software toolkit from NVIDIA providing a high-level abstraction that enables our code to run on the GPU. If you want to run your system on a GPU, you need to install CUDA. While CUDA can be installed manually for system-wide use, in this case, we only need it for TensorFlow. Fortunately, TensorFlow automatically installs the relevant CUDA dependencies. After this, install Jupyter Notebook using the following command: pip install notebook Open Jupyter Notebook using the following command: Jupyter notebook After running Jupyter Notebook, copy the link shown in the wsl terminal and paste it into your browser. After pasting the link into the browser, you will see this page. Now you can create a new notebook and test your code. import tensorflow as tfgpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices(‘GPU’)print(gpus) details = tf.config.experimental.get_device_details(gpus[0])print(f”Device: {gpus[0].name}, Name: {details.get(‘device_name’, ‘Unknown’)}”) Now you have successfully set up TensorFlow with GPU. When you run your code, it will automatically use the GPU. In TensorFlow, you don’t need to manually specify the GPU in your code, as shown in the sample output below. Conclusion Setting up TensorFlow with GPU can significantly accelerate deep learning tasks. In this guide, we walked through the process of installing WSL, Miniconda, and TensorFlow GPU, ensuring that your code runs efficiently on the available GPU. Unlike some frameworks, TensorFlow automatically utilizes the GPU without requiring explicit configuration in your code. With this setup, you are now ready to train and test deep learning models with improved performance. Join thousands of data leaders on the AI newsletter. Join over 80,000 subscribers and keep up to date with the latest developments in AI. From research to projects and ideas. If you are building an AI startup, an AI-related product, or a service, we invite you to consider becoming a sponsor. Published via Towards AI