Learning Machine Learning
Machine learning is one of the most interesting and advancing aspects of engineering and computer science. It shows you the potential of machines in our modern day world. Machine learning is essentially making a machine learn to perform different tasks by feeding enormous amounts of data. To accomplish this, there are multiple algorithms used for machines to learn and adapt to perform a task easier with new inputs. One of the algorithms is called neural networks. A Neural Network (usually abbreviated as NN) is a learning algorithm that is very similar to a biological neural network. Before going into depth of a neural network (more in depth posts coming up), lets take a look at what kinds of machine learning problems there are and their classifications:
- Supervised Learning: Supervised learning is when the computer takes in inputs and predicts a particular output. The machine is first presented with many inputs, and it gradually learns a pattern or rule that maps the inputs to the outputs. This process of training is continued until the computer is sufficient enough to predicted even further complicated inputs. The computer is slowly learning an algorithm based on a function that maps an input to an output. Regression and Classification are two types of supervised learning.
- Regression: Regression is a supervised learning problem which gather inputs and predicts outputs that are rather continuous. An example would be predicting the stock prices using data from the past.
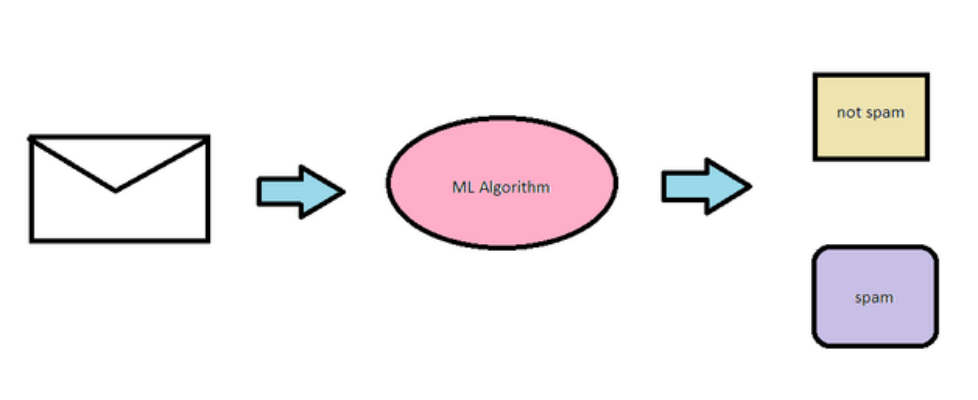
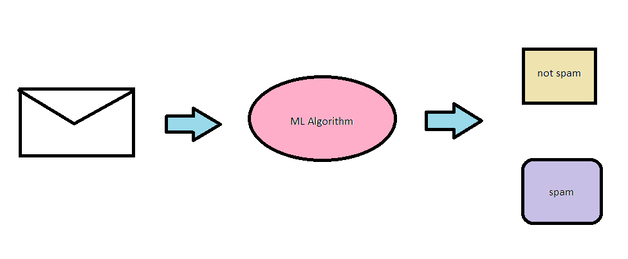
- Classification: Classification is a supervised learning problem which gathers inputs to predict an output which is classified into groups. For example, spam detection would be a classification problem since the outputs have two categories: spam or not spam.
An example of Supervised learning is segregating spam and not spam mail. The computer takes in bunch of mail, and uses a machine learning algorithm to assign the mail one output; either spam, or not spam. The machine does this by learning from previous examples of inputs and it grasps the algorithm or pattern to use for future inputs.
- Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning is when we leave the computer alone to find the structure of the inputs. It is essentially when none of the input data is labelled. It is when the computer makes inferences of the data without have a label associated with it.
Like
0
Liked
Liked