Big O Notation in Data Structure: Meaning, Examples & Graph Explained
When learning data structures and algorithms, one concept every learner encounters early on is Big O notation. It forms the backbone of analysing and comparing algorithms based on their speed and memory usage. In simple terms, Big O notation in data structure describes how the running time or space requirement of an algorithm grows as the size of the input increases. It does not measure time in seconds or microseconds, it measures growth rate.
As computer scientist Donald Knuth once said, “Premature optimization is the root of all evil.” To optimise efficiently, one must first understand how fast an algorithm grows with input size, that’s where Big O notation becomes essential.
Overview
- Big O notation in data structure describes algorithm time/space complexity upper bounds as input size grows.
- What is Big O notation in data structure? Mathematical way to show asymptotic growth rate, focusing on worst-case.
- Example of Big O notation in data structure: Linear search O(n), binary search O(log n), bubble sort O(n²).
- Big O notation graph visualises growth: O(1) flat, O(n²) steep, O(2ⁿ) exponential.
- Big O notation calculator estimates complexity from code/expressions, ignores constants/lower terms.
- Big O notation cheat sheet: O(1) constant, O(n) linear, O(n log n) sorting, O(n!) factorial.

What is Big O Notation in Data Structure?
Big O notation is a mathematical representation used to describe the time complexity and space complexity of algorithms. It captures the asymptotic behaviour, that is, how an algorithm’s resource use scales as input size () increases.
Imagine you have a program that sorts 10, 100, or 10,000 numbers. You may not care how long it takes for 10 numbers, but for 10,000 numbers, you’ll definitely notice the difference. Big O provides a scientific way to predict that growth.
Why is Big O Notation Important?
- It helps compare algorithms independent of system hardware.
- It highlights scalability, how performance changes with large inputs.
- It shows the worst-case scenario, which is vital for performance guarantees.
- Developers and data scientists rely on it when designing large systems or processing millions of records.
So, if two algorithms solve the same task, Big O tells which will handle larger inputs better and faster.
Common Types of Big O Notation
Let’s break down the most common complexities seen in algorithms here:
| Big O Notation | Common Name | Examples |
| O(1) | Constant time | Accessing an element in an array by index. |
| O(log n) | Logarithmic time | Binary search on a sorted list. |
| O(n) | Linear time | Traversing all elements in a list. |
| O(n log n) | Linearithmic time | Merge Sort, Quick Sort average case. |
| O(n²) | Quadratic time | Nested loops (e.g., Bubble Sort). |
| O(2ⁿ) | Exponential time | Recursive algorithms like solving the Travelling Salesman Problem. |
| O(n!) | Factorial time | Checking all permutations (e.g., generating all sequences). |
The smaller the complexity, the better the algorithm scales.
Example of Big O Notation in Data Structure
Let’s take a simple example to see how Big O analysis works. Suppose you want to search for a number in an unsorted list. Here, you might have to look through the list element by element.
for each element in the list:
if element == value:
return true
return false
- This algorithm checks each element, its time complexity is O(n), because in the worst case, every element must be checked once.
- In contrast, if the list were sorted and you used binary search, the time complexity would drop to O(log n).
As you can see, a small change in approach can significantly improve efficiency. That’s the power of Big O analysis.

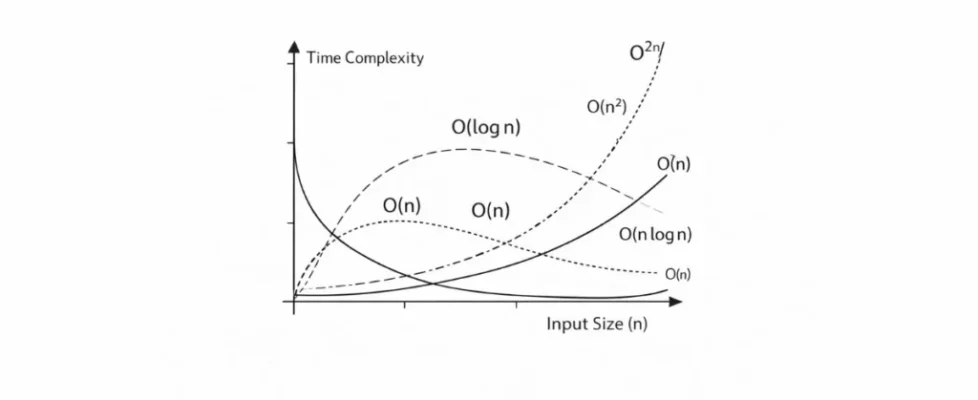
Big O Notation Graph: Visualising Growth
If you plot different Big O functions on a graph, you clearly see how they scale.
- O(1) remains flat,constant time, regardless of input size.
- O(log n) grows slowly.
- O(n) grows linearly,double the input, double the time.
- O(n²) grows steeply, unsuitable for large inputs.
This is why data scientists often use a Big O notation graph to visualise which algorithms handle large data efficiently. Tools like a Big O notation calculator can also help you estimate and visualise time complexity for specific code snippets.
Analysing Algorithms: How to Find Big O
To determine the Big O of an algorithm, follow these simple steps:
- Identify the basic operation: Find what operation contributes most to execution time (e.g., comparisons or assignments).
- Count repetitions: Estimate how many times the core operation repeats based on input size.
- Drop constants and lower-order terms: Big O focuses only on dominant terms, details like 3n+5 simplify to 0(n).
- Consider worst case: In data structure analysis, we focus on the upper limit of complexity, assuming the worst-case input.
This gives a clear picture of how performance scales, irrespective of environment or implementation language.
Read More: Association in Machine Learning: Rules, Algorithms & Use
Big O Notation Cheat Sheet: Quick Reference
Here’s a simple Big O notation cheat sheet that learners often keep handy:
- O(1): Constant – Best possible.
- O(log n): Logarithmic – Efficient searching.
- O(n): Linear – Simple iteration.
- O(n log n): Efficient sorting.
- O(n²): Nested iterations, avoid for large data.
- O(2ⁿ): Exponential, grows too fast.
- O(n!): Factorial, impractical for big n.
Remember: for large data structures, even a small improvement in Big O means huge time savings.
Big O: Here’s An Easy Way to Understand!
Think of Big O like traffic on a highway.
- O(1): You’re driving on an empty road , smooth and fast.
- O(n): Each extra car slows you down linearly.
- O(n²): Every new car interacts with every other , chaos!
This analogy helps explain why software engineers avoid algorithms that scale poorly when data grows.
Common Mistakes When Interpreting Big O
Many beginners misunderstand Big O as measuring “speed.” But it reflects growth rate, not raw performance. For instance, a slower algorithm can outperform a fast
one for small inputs. Always pair Big O with empirical analysis, benchmark code to see real-world performance, especially for small.
Uses of Big O in Data Structure Design
Big O notation helps when:
- Choosing between hash tables (O(1) lookup) and linked lists (O(n) lookup).
- Deciding which sorting algorithm to use for different use cases.
- Designing scalable solutions for applications dealing with large datasets or real-time analytics.
As per an ACM Computing Survey (2023), “algorithms optimised for average Big O performance cut processing times by up to 70% in large-scale systems.”
On A Final Note…
Big O notation is not just theory; it’s a guiding principle for building efficient programs and scalable systems. For anyone studying data structures and algorithms, mastering this notation means developing the intuition to predict performance even before running the code.
As the saying goes, “An algorithm must be seen to be believed.” By learning how to read and apply Big O, you start to see not just how your code works, but how well it works when the world gets big.
FAQs
1. What is Big O notation in data structure?
Big O notation describes how the running time or memory usage of an algorithm changes with the size of its input. It helps measure efficiency and scalability of code.
2. What is an example of Big O notation in data structure?
A linear search in an array takes O(n) time, because every element might need to be checked once. A binary search takes O(log n), which is faster for large inputs.
3. How do I calculate Big O of an algorithm?
Count how many times the main operation runs relative to input size, ignore constants and minor terms, and express the growth in standard Big O form.
4. What is a Big O notation graph?
It’s a graph showing how different time complexities increase with input size, helping visualise how algorithms scale.
5. What is a Big O notation calculator?
It’s an online or tool-based utility that helps estimate the Big O time complexity of algorithms based on code patterns or execution counts.
6. Where can I find a Big O notation cheat sheet?
Many coding platforms and developer blogs provide a quick reference sheet summarising common complexities like O(1), O(n), and O(n²).