Association in Machine Learning: Rules, Algorithms & Use
Making sense of large volumes of data has become a critical challenge for modern organizations. Data is generated daily from transactions, websites, and healthcare systems, but its true value lies in the patterns hidden within it.
Association in machine learning uncovers these patterns by identifying relationships between frequently occurring items, without relying on labeled datasets. This technique falls under unsupervised learning, where models explore data independently.
In this blog, we dive into what association in machine learning really means, unpack association rules in machine learning, see how it fits into unsupervised learning, compare it with clustering, look at key algorithms like Apriori and FP-Growth, explore its applications, and even show you how to get started with Python code.
All this sits within unsupervised learning, where models freely explore the data on their own – so, get ready for some learning!
Table of Contents
- What is Association in Machine Learning?
What is Association in Machine Learning?
Association in machine learning looks for relationships in large datasets, like which products customers buy together. Think of it as spotting “if this, then that” patterns in everyday shopping data. For example, if people buy bread, they might also pick up butter – think about it.
Data scientists use it to dig into transaction records or user behaviour.
Association rule learning identifies hidden correlations in databases by applying some measure of interestingness,” as noted in machine learning glossaries.

Have you ever wondered why supermarkets place certain items near each other?
- It works on transactional data, such as sales receipts.
- No need for predefined outcomes; the data reveals the stories.
- Common in retail but applies to healthcare and web usage too.
Association Rules in Machine Learning Explained
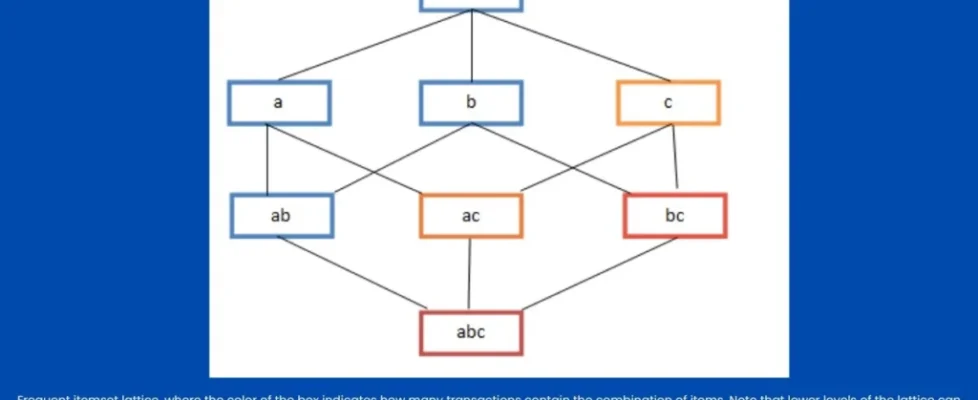
Association rules in machine learning follow the form X -> Y, where X leads to Y. These rules show how often items pair up in datasets. They rely on three main measures: support, confidence, and lift.
Support counts how frequent an itemset is across transactions. Confidence shows the strength of the rule, like the chance Y follows X. Lift checks if the link beats random chance – a value over 1 means a real connection.
Pointers for quick grasp:
- Support: Percentage of transactions with the itemset.
- Confidence: How often the rule holds true.
- Lift: Rule strength beyond independence.
Questions like “What items pair with milk?” drive these rules. In one study, rules helped retailers boost sales by 10-20% through better layouts.
How Association Fits in Unsupervised Machine Learning
Association in unsupervised machine learning thrives without labels, grouping items by co-occurrence. It mines patterns from raw data, making it ideal for exploration. Unlike supervised methods, it finds surprises in the data.
“Association learning is a type of unsupervised learning, which means that it does not require any prior knowledge of the data,” experts point out. This opens doors for new insights in big datasets. Proof comes from market basket analysis, where rules predict buys accurately. Indian e-commerce sites use it to suggest combos, lifting cart values.
Key Algorithms for Association Rules
Two main algorithms power association rules: Apriori and FP-Growth.
Apriori scans data multiple times to build frequent itemsets. It prunes rare items early, using the rule that subsets of frequent sets are frequent too. Steps include:
- Find single items meeting minimum support.
- Join them into pairs, check support.
- Repeat for larger sets, generate rules.
FP-Growth builds a compact tree (FP-tree) from data, mining patterns faster without candidate generation. It suits huge datasets better than Apriori.
Example with 5 transactions (min support 40%, confidence 70%):
- Transactions: {Bread, Butter, Milk}, {Bread, Butter}, {Beer, Cookies, Diapers}, {Milk, Diapers, Bread, Butter}, {Beer, Diapers}.
- Frequent itemsets: Bread (3), Butter (3), Diapers (3), etc.
- Rule: {Bread, Butter} → {Milk} (confidence checks out).

Difference Between Clustering and Association in Machine Learning
Clustering and association both belong to unsupervised learning but serve different goals. Clustering groups similar data points into clusters based on distance or features. Association finds rules linking specific items.
| Aspect | Clustering | Association |
| Purpose | Groups similar data points together | Finds relationships between items that occur together |
| Main Question | “Which data points are similar?” | “Which items are frequently linked?” |
| Output | Clusters (groups of similar records) | Rules like If A → then B |
| Data Focus | Overall similarity or distance | Frequency and co-occurrence |
| Common Use Cases | Customer segmentation, image grouping | Market basket analysis, recommendation systems |
| Example | Grouping customers based on buying behavior | Finding that customers who buy bread often buy butter |
| Typical Algorithms | K-Means, Hierarchical Clustering, DBSCAN | Apriori, FP-Growth |
“Clustering identifies hidden patterns without predetermined variables, while association needs predefined items,” as per learning resources. Clustering suits images or users; association excels in transactions.
Why does this matter? Clustering segments markets broadly; association pinpoints product pairs precisely.
Read More: 3 Vs of Big Data Explained: Volume, Velocity, Variety | Big Data Analytics Courses
Applications of Association Rules
Retailers use association rules for market basket analysis, placing bread near butter. Recommendation engines on Flipkart or Amazon suggest “people who bought this also bought that.” In healthcare, rules link symptoms to diseases, aiding diagnosis. Telecom firms spot call patterns for better service; insurance detects fraud via odd combos.
- E-commerce: Boost conversions by 15% with smart suggestions.
- Inventory: Stock pairs together to cut costs.
- Fraud: Flag unusual transaction links.
Indian businesses, from BigBasket to hospitals, apply these daily, for gains.
How to Get Started with Association in Python?
Use libraries like mlxtend for Apriori. Load data, set min_support=0.3, run apriori(), then association_rules(). Simple code reveals rules fast. Tools like WEKA or Orange offer no-code options. Start with sample grocery data to see patterns emerge.

On A Final Note…
Association in machine learning offers a straightforward way to uncover valuable patterns from raw data, from retail recommendations to healthcare insights. Throughout this blog, we explored its core concepts, rules, algorithms, and clear distinctions from clustering, along with practical steps to implement it yourself.
Key takeaways include how association rules like X -> Y power real decisions through metrics such as support and confidence, while algorithms like Apriori and FP-Growth make it scalable for large datasets. Whether you segment markets with clustering or link products via association, choosing the right tool depends on your data type and goals, transactional data calls for association, feature-rich data for clustering.
Indian businesses, from e-commerce giants to local hospitals already gain from these techniques daily. Start experimenting with Python libraries on sample datasets to see patterns emerge in your own work. The next time you spot related product suggestions online, know that association rules likely drive them.
FAQs
-
What is association in machine learning?
Association in machine learning finds patterns where items appear together in data, using rules like X -> Y.
-
What are association rules in machine learning?
Association rules in machine learning are if-then statements showing item relationships, measured by support, confidence, and lift.
-
What is the difference between clustering and association in machine learning?
Clustering groups similar data points; association uncovers specific item relationships via rules.
-
Is association part of unsupervised machine learning?
Yes, association in unsupervised machine learning discovers patterns without labels.
-
What algorithms use association rules?
Apriori and FP-Growth generate association rules efficiently.