Reference Architecture for Private AI on Azure: Designing Secure, Compliant, Hybrid LLM Systems
Introduction: The Rise of Private AI
Over the past two decades working in cloud architecture, I’ve witnessed several technology waves, but Private AI marks a fundamental shift in how enterprises will operate for the next decade. Unlike fleeting trends, Private AI is reshaping the structural dynamics of enterprise operations, emphasizing trust, security, and compliance.
Every organization I work with wants the same outcome: Use AI to accelerate the business without compromising security, compliance, or data sovereignty.
“Private AI isn’t about the model. It’s about trust.” I’ve repeated that line in more boardrooms and architecture reviews than I can count. The technology is impressive, but the real challenge is designing AI systems that respect enterprise boundaries — security, compliance, and data governance — without slowing innovation.
Azure has quietly become one of the most capable platforms for building secure, compliant, hybrid LLM systems. Not because it has the flashiest models, but because it understands the realities of enterprise architecture: legacy systems, regulatory pressure, hybrid networks, and the constant tug‑of‑war between innovation and risk.
This article walks through the reference architecture I use with customers who are ready to move beyond prototypes and into production. It’s based on real deployments, real constraints, and real lessons learned.
This is not theory. It’s the pattern that consistently works in real‑world, regulated, globally distributed environments.
1. Core Principles of Private AI on Azure
Callout: If your AI architecture doesn’t start with security and compliance, it’s already off track.
After twenty years in this field, a few principles always hold up:
1. Keep sensitive data inside your trust boundary
Your LLM can run in Azure, but your data should remain where you control it — Azure, on‑prem, or hybrid.
2. Retrieval beats fine‑tuning for most enterprise use cases
RAG is safer, cheaper, and easier to govern.
3. Assume hybrid from day one
Your data is scattered. Your architecture should embrace that, not fight it.
4. Build for auditability
AI systems must be explainable, observable, and governed.
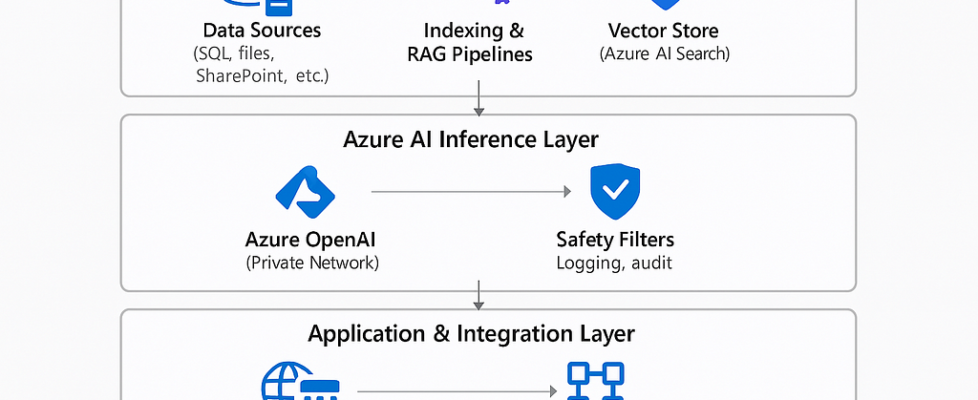
2. High‑Level Reference Architecture
Here’s the architecture I typically sketch on a whiteboard when kicking off a Private AI project.

3. Security: The Non‑Negotiable Foundation
If your Azure OpenAI endpoint is public, your architecture is not Private AI.
Security is where most AI projects succeed or fail. Azure provides powerful capabilities, but you must assemble them with discipline.
1. Network Isolation
- Use Private Endpoints for Azure OpenAI, Azure AI Search, Storage, and App Services
- Disable public access entirely
- Route outbound traffic through Azure Firewall or an NVA if required.
Reference: [3]
2. Identity & Access
- Use Managed Identities end-to-end
- Apply Conditional Access for human access
- Enforce least-privilege access to vector stores and pipelines
Reference: [4]
3. Data Protection
- Enable Customer Managed Keys (CMK)
- Use Confidential Computing for sensitive workloads
- Keep raw data inside your trust boundary — only embeddings should leave.
Reference: [5]
4. Compliance
- Azure OpenAI already supports SOC, ISO, HIPAA, and more
- Add prompt logging, audit logging, and content filtering on top
4. Deep Dive: Hybrid RAG Architecture Backbone of Private AI
Most enterprises don’t have the luxury of centralizing all their data. Hybrid RAG is the backbone of Private AI.

5. Inference Layer: Azure OpenAI in a Private Network
Why this pattern works
- Sensitive data stays within the enterprise
- Indexing scales independent of inference
- Clean separation between model and data
Technical considerations
- Use delta indexing to avoid full reprocessing
- Store metadata with embeddings
- Use semantic rankers to improve retrieval quality
References: [6]
Callout: Treat the model as a stateless inference engine. The intelligence comes from your data, not the model.
Best Practices
- Deploy Azure OpenAI with VNet integration
- Add content filters and custom safety rules
- Securely log prompts and completions
- Use prompt templates for consistency
Model Selection Guidance
- GPT‑4 class models→ reasoning, copilots, analysis
- Smaller models → classification, extraction, routing
- Vision models → document understanding, OCR, multimodal flows
Reference: [8]
6. Application Layer: Where AI Meets the Business
This is where the architecture becomes real for end users.
Common Patterns
- Internal copilots for employees
- AI‑powered search portals
- Workflow automation with Logic Apps
- Chatbots integrated into Teams
- Plugins for ERP, CRM, and line‑of‑business systems
Application Integration Flow

7. Observability, Governance, and Lifecycle
Pull‑quote: “If you can’t observe it, you can’t trust it. If you can’t govern it, you can’t scale it.”
What to Track
- Prompt/response logs
- Latency and throughput
- Token consumption
- RAG hit/miss ratios
- Data freshness
- Safety filter triggers
Governance Essentials
- Establish an AI Review Board
- Maintain model cards
- Track data lineage
- Version prompts, embeddings, and pipelines
10 Common Mistakes in Private AI Projects
A quick list I wish every team taped to their monitor.
- Leaving Azure OpenAI endpoints public
- Trying to fine‑tune when RAG is enough
- Indexing entire data lakes instead of curating sources
- Skipping metadata enrichment in vector stores
- Not versioning prompts or embeddings
- Treating AI like a single app instead of a platform capability
- Ignoring token cost modeling
- Allowing “shadow AI” tools to proliferate
- Underestimating the need for observability
- Not involving security early — and often
8. Final Thoughts
Private AI isn’t a single project — it’s a capability. The architecture above gives you a foundation that scales with your organization, respects your security posture, and keeps you compliant without slowing innovation.
If you build it right, your teams get the power of modern LLMs while your data stays exactly where it belongs: under your control.
And that’s the real promise of Private AI on Azure.
Reference Architecture for Private AI on Azure: Designing Secure, Compliant, Hybrid LLM Systems was originally published in Towards AI on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.